React Localization - Internationalize with i18next
Overcoming the language barrier for users who use your software is an important topic. English is no longer the universal language of the internet. As of March 2020, only 25.9% of internet users were English speakers. The chances are high that your users will skip past your website if non-localized. Therefore, without a multilingual website you might miss out on a large share of potential users.
In the JavaScript ecosystem, there are a lot of internationalization frameworks. Here you can find some details about some JavaScript internationalization frameworks. In this article, we will be using the i18next framework to internationalize a React app. This step-by-step guide is for you if you're looking for a way to create an internationalized React app (with or without Create React App).
This post was originally published in 2021 and updated on December 23, 2025 to reflect changes in the i18next and React ecosystem.
TOC
- So first of all: "Why i18next?"
- What's new (since 2021)?
- Let's get into it...
- 🎉🥳 Congratulations 🎊🎁
Streamline your i18next setup process with this step-by-step guide. Get your localization framework up and running in no time and ensure smooth language transitions for your users. Follow the instructions and avoid any setup complications for your next international project.
So first of all: "Why i18next?"
When it comes to React localization, one of the most popular is i18next with its react extension react-i18next, and for good reasons:
i18next was created in late 2011. It's older than most of the libraries you will use nowadays, including your main frontend technology (React, Angular, Vue, ...).
➡️ sustainable
Based on how long i18next already is available open source, there is no real i18n case that could not be solved with i18next.
➡️ mature
i18next can be used in any javascript (and a few non-javascript - .net, elm, iOS, android, ruby, ...) environment, with any UI framework, with any i18n format, ... the possibilities are endless.
➡️ extensible
There is a plenty of features and possibilities you'll get with i18next compared to other regular i18n frameworks.
➡️ rich
Here you can find more information about why i18next is special and how it works.
What's new (since 2021)?
In 2025, i18next introduced a powerful new feature: the typescript selector API. This brings typesafe access to your translations and enables strong autocomplete support. You can learn more about it in How to translate with i18next: typescript and Typesafe i18next with the new typescript selector API.
In 2024, i18next introduced a new plugin to help you integrate i18next into Express apps: i18next-http-middleware. If you're working with React in an Express environment, this can be a useful addition.
Need professional translation management? See How to translate with i18next: the CLI for a streamlined workflow.
Interested in a continuous localization workflow? Check out Modern continuous localization.
Let's get into it (react-i18next)...
Prerequisites
Make sure you have Node.js and npm installed. It's best, if you have some experience with simple HTML, JavaScript and basic React.js, before jumping to react-i18next - the powerful React i18n framework. This react-i18next localization example is not intended to be a React beginner tutorial.
Getting started
Take your own React project or create a new one, i.e. with create-react-app.
npx create-react-app my-app

We are going to adapt the app to detect the language according to the user’s preference. And we will create a language switcher to make the content change between different languages.
Let's install some i18next dependencies:
npm install i18next react-i18next i18next-browser-languagedetector
Let's prepare an i18n.js file:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
i18n
// detect user language
// learn more: https://github.com/i18next/i18next-browser-languageDetector
.use(LanguageDetector)
// pass the i18n instance to react-i18next.
.use(initReactI18next)
// init i18next
// for all options read: https://www.i18next.com/overview/configuration-options
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false, // not needed for react as it escapes by default
},
resources: {
en: {
translation: {
// here we will place our translations...
}
}
}
});
export default i18n;Let's import that file somewhere in our index.js file:
For React >= 18.0.0 use:
import React from 'react';
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
import './index.css';
import App from './App';
// import i18n (needs to be bundled ;))
import './i18n';
const root = createRoot(document.getElementById('root'))
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);For older React versions use:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './index.css';
import App from './App';
// import i18n (needs to be bundled ;))
import './i18n';
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);Now let's try to move some hard coded text out to the translations.
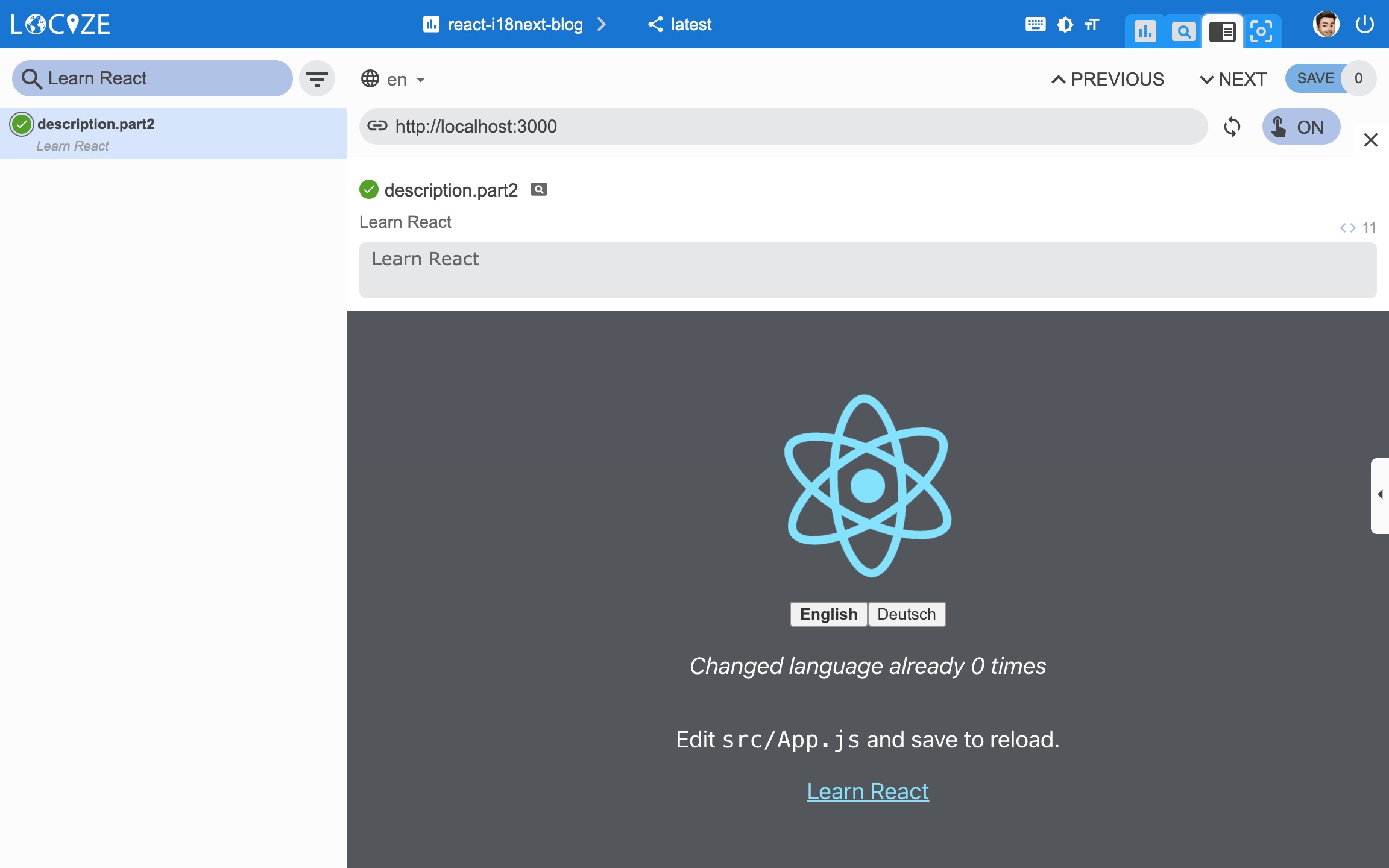
We have used the Trans component for the first text and the useTranslation hook for the second text:
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
import { useTranslation, Trans } from 'react-i18next';
function App() {
const { t } = useTranslation();
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<p>
<Trans i18nKey="description.part1">
Edit <code>src/App.js</code> and save to reload.
</Trans>
</p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
{t('description.part2')}
</a>
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App;There is some more effort necessary if you wish to use High-Order-Components (HOC). Another option in this situation is to use withTranslation HOC.
The texts are now part of the translation resources:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
i18n
// detect user language
// learn more: https://github.com/i18next/i18next-browser-languageDetector
.use(LanguageDetector)
// pass the i18n instance to react-i18next.
.use(initReactI18next)
// init i18next
// for all options read: https://www.i18next.com/overview/configuration-options
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false, // not needed for react as it escapes by default
},
resources: {
en: {
translation: {
description: {
part1: 'Edit <1>src/App.js</1> and save to reload.',
part2: 'Learn React'
}
}
}
}
});
export default i18n;Language Switcher
Now let's define a language switcher:
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
import { useTranslation, Trans } from 'react-i18next';
const lngs = {
en: { nativeName: 'English' },
de: { nativeName: 'Deutsch' }
};
function App() {
const { t, i18n } = useTranslation();
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<div>
{Object.keys(lngs).map((lng) => (
<button key={lng} style={{ fontWeight: i18n.resolvedLanguage === lng ? 'bold' : 'normal' }} type="submit" onClick={() => i18n.changeLanguage(lng)}>
{lngs[lng].nativeName}
</button>
))}
</div>
<p>
<Trans i18nKey="description.part1">
Edit <code>src/App.js</code> and save to reload.
</Trans>
</p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
{t('description.part2')}
</a>
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App;And also add some translations for the new language:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
i18n
// detect user language
// learn more: https://github.com/i18next/i18next-browser-languageDetector
.use(LanguageDetector)
// pass the i18n instance to react-i18next.
.use(initReactI18next)
// init i18next
// for all options read: https://www.i18next.com/overview/configuration-options
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false, // not needed for react as it escapes by default
},
resources: {
en: {
translation: {
description: {
part1: 'Edit <1>src/App.js</1> and save to reload.',
part2: 'Learn React'
}
}
},
de: {
translation: {
description: {
part1: 'Ändere <1>src/App.js</1> und speichere um neu zu laden.',
part2: 'Lerne React'
}
}
}
}
});
export default i18n;
🥳 Awesome, you've just created your first language switcher!
Thanks to i18next-browser-languagedetector now it tries to detect the browser language and automatically use that language if you've provided the translations for it. The manually selected language in the language switcher is persisted in the localStorage, next time you visit the page, that language is used as preferred language.
How to get the current language?
Since i18next v21 there is i18next.resolvedLanguage.
It is set to the current resolved language and it can be used as primary used language, for example in a language switcher.
If your detected language for example is en-US and you provided translations only for en (fallbackLng) instead i18next.resolvedLanguage will return en.
i18next.language vs. i18next.languages vs. i18next.resolvedLanguage
/* language */
i18next.language;
// Is set to the current detected or set language.
/* languages */
i18next.languages;
// Is set to an array of language codes that will be used to look up the translation value.
// When the language is set, this array is populated with the new language codes.
// Unless overridden, this array is populated with less-specific versions of that code for fallback purposes, followed by the list of fallback languages
// initialize with fallback languages
i18next.init({
fallbackLng: ["es", "fr", "en-US", "dev"]
});
// change the language
i18next.changeLanguage("en-US-xx");
// new language and its more generic forms, followed by fallbacks
i18next.languages; // ["en-US-xx", "en-US", "en", "es", "fr", "dev"]
// change the language again
i18next.changeLanguage("de-DE");
// previous language is not retained
i18next.languages; // ["de-DE", "de", "es", "fr", "en-US", "dev"]
/* resolvedLanguage */
i18next.resolvedLanguage;
// Is set to the current resolved language.
// It can be used as primary used language,
// for example in a language switcher.Interpolation and Pluralization
i18next goes beyond just providing the standard i18n features. But for sure it's able to handle plurals and interpolation.
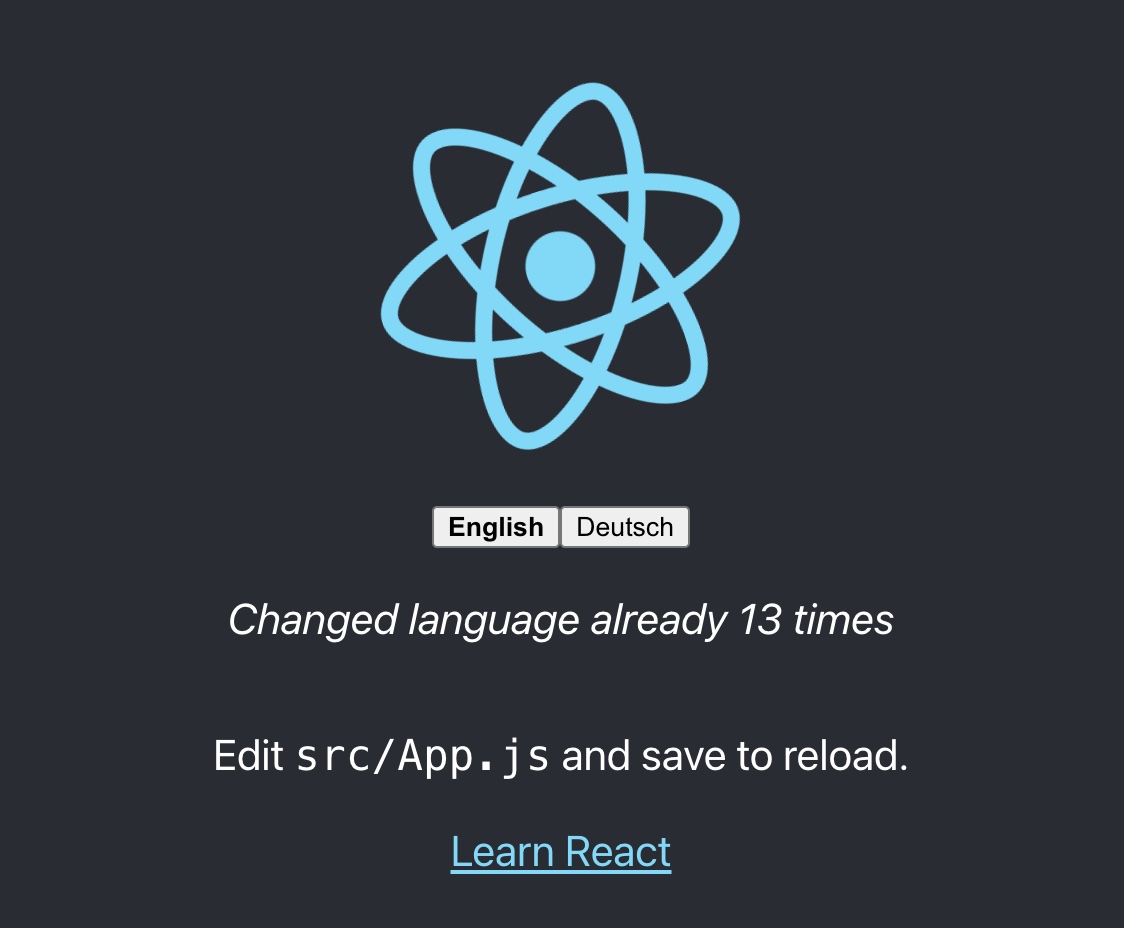
Let's count each time the language gets changed:
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
import { useTranslation, Trans } from 'react-i18next';
import { useState } from 'react';
const lngs = {
en: { nativeName: 'English' },
de: { nativeName: 'Deutsch' }
};
function App() {
const { t, i18n } = useTranslation();
const [count, setCounter] = useState(0);
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<div>
{Object.keys(lngs).map((lng) => (
<button key={lng} style={{ fontWeight: i18n.resolvedLanguage === lng ? 'bold' : 'normal' }} type="submit" onClick={() => {
i18n.changeLanguage(lng);
setCounter(count + 1);
}}>
{lngs[lng].nativeName}
</button>
))}
</div>
<p>
<i>{t('counter', { count })}</i>
</p>
<p>
<Trans i18nKey="description.part1">
Edit <code>src/App.js</code> and save to reload.
</Trans>
</p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
{t('description.part2')}
</a>
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App;...and extending the translation resources:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
i18n
.use(LanguageDetector)
.use(initReactI18next)
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false,
},
resources: {
en: {
translation: {
description: {
part1: 'Edit <1>src/App.js</1> and save to reload.',
part2: 'Learn React'
},
counter_one: 'Changed language just once',
counter_other: 'Changed language already {{count}} times'
}
},
de: {
translation: {
description: {
part1: 'Ändere <1>src/App.js</1> und speichere um neu zu laden.',
part2: 'Lerne React'
},
counter_one: 'Die Sprache wurde erst ein mal gewechselt',
counter_other: 'Die Sprache wurde {{count}} mal gewechselt'
}
}
}
});
export default i18n;Based on the count value i18next will choose the correct plural form. Read more about pluralization and interpolation in the official i18next documentation.
💡 i18next is also able to handle languages with multiple plural forms, like arabic:
// translation resources:
{
"key_zero": "zero",
"key_one": "singular",
"key_two": "two",
"key_few": "few",
"key_many": "many",
"key_other": "other"
}
// usage:
t('key', {count: 0}); // -> "zero"
t('key', {count: 1}); // -> "singular"
t('key', {count: 2}); // -> "two"
t('key', {count: 3}); // -> "few"
t('key', {count: 4}); // -> "few"
t('key', {count: 5}); // -> "few"
t('key', {count: 11}); // -> "many"
t('key', {count: 99}); // -> "many"
t('key', {count: 100}); // -> "other"Why are my plural keys not working?
Are you seeing this warning in the development console (debug: true)?
i18next::pluralResolver: Your environment seems not to be Intl API compatible, use an Intl.PluralRules polyfill. Will fallback to the compatibilityJSON v3 format handling.
With v21 i18next streamlined the suffix with the one used in the Intl API. In environments where the Intl.PluralRules API is not available (like older Android devices), you may need to polyfill the Intl.PluralRules API. In case it is not available it will fallback to the i18next JSON format v3 plural handling. And if your json is already using the new suffixes, your plural keys will probably not be shown.
tldr;
npm install intl-pluralrules
import 'intl-pluralrules'Formatting
Starting with i18next v21.3.0, built-in formatters are available for formatting numbers, dates, lists, and more using the Intl API. For details and advanced usage, see the official i18next formatting documentation.
Now, let’s check out how we can use different date formats with the help of i18next and Luxon to handle date and time.
{
"key": "Some format {{value, formatname}}",
"keyWithOptions": "Some format {{value, formatname(option1Name: option1Value; option2Name: option2Value)}}"
}You can pass options as a semicolon-delimited list.
JavaScript usage:
// JSON
{
"intlNumber": "Some {{val, number}}",
"intlNumberWithOptions": "Some {{val, number(minimumFractionDigits: 2)}}"
}
i18next.t($ => $.intlNumber, { val: 1000 });
// --> Some 1,000
i18next.t($ => $.intlNumber, { val: 1000.1, minimumFractionDigits: 3 });
// --> Some 1,000.100
i18next.t($ => $.intlNumber, { val: 1000.1, formatParams: { val: { minimumFractionDigits: 3 } } });
// --> Some 1,000.100
i18next.t($ => $.intlNumberWithOptions, { val: 2000 });
// --> Some 2,000.00
i18next.t($ => $.intlNumberWithOptions, { val: 2000, minimumFractionDigits: 3 });
// --> Some 2,000.000You can override the language by passing lng or locale in the options:
i18next.t($ => $.intlNumber, { val: 1000.1, lng: 'de' });
i18next.t($ => $.intlNumber, { val: 1000.1, formatParams: { val: { locale: 'de' } } });Adding custom format functions:
// after i18next.init(options);
i18next.services.formatter.add('lowercase', (value, lng, options) => value.toLowerCase());
i18next.services.formatter.add('underscore', (value, lng, options) => value.replace(/\s+/g, '_'));Add your custom format function after the i18next.init() call.
Built-in formats:
- Number:
number - Currency:
currency - DateTime:
datetime - RelativeTime:
relativetime - List:
list
See the i18next formatting documentation for more examples and options.
Now, let’s check out how we can use different date formats with the help of i18next and Luxon to handle date and time.
npm install luxon
We like to have a footer displaying the current date:
import './Footer.css';
const Footer = ({ t }) => (
<div className="Footer">
<div>{t('footer.date', { date: new Date() })}</div>
</div>
);
export default Footer;
// imported in our App.js and used like this
// <Footer t={t} />Now import Luxon and define a format function (as documented in the formatting docs), then add the new translation key:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
import { DateTime } from 'luxon';
i18n
.use(LanguageDetector)
.use(initReactI18next)
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false,
// format: (value, format, lng) => { // legacy usage
// if (value instanceof Date) {
// return DateTime.fromJSDate(value).setLocale(lng).toLocaleString(DateTime[format])
// }
// return value;
// }
},
resources: {
en: {
translation: {
description: {
part1: 'Edit <1>src/App.js</1> and save to reload.',
part2: 'Learn React'
},
counter_one: 'Changed language just once',
counter_other: 'Changed language already {{count}} times',
footer: {
date: 'Today is {{date, DATE_HUGE}}'
}
}
},
de: {
translation: {
description: {
part1: 'Ändere <1>src/App.js</1> und speichere um neu zu laden.',
part2: 'Lerne React'
},
counter_one: 'Die Sprache wurde erst ein mal gewechselt',
counter_other: 'Die Sprache wurde {{count}} mal gewechselt',
footer: {
date: 'Heute ist {{date, DATE_HUGE}}'
}
}
}
}
});
// new usage
i18n.services.formatter.add('DATE_HUGE', (value, lng, options) => {
return DateTime.fromJSDate(value).setLocale(lng).toLocaleString(DateTime.DATE_HUGE)
});
export default i18n;😎 Cool, now we have a language specific date formatting!
English:

German:

Context
What about a specific greeting message based on the current day time? i.e. morning, evening, etc. This is possible thanks to the context feature of i18next.
Let's create a getGreetingTime function and use the result as context information for our footer translation:
import { DateTime } from 'luxon';
import './Footer.css';
const getGreetingTime = (d = DateTime.now()) => {
const split_afternoon = 12; // 24hr time to split the afternoon
const split_evening = 17; // 24hr time to split the evening
const currentHour = parseFloat(d.toFormat('hh'));
if (currentHour >= split_afternoon && currentHour <= split_evening) {
return 'afternoon';
} else if (currentHour >= split_evening) {
return 'evening';
}
return 'morning';
}
const Footer = ({ t }) => (
<div className="Footer">
<div>{t('footer.date', { date: new Date(), context: getGreetingTime() })}</div>
</div>
);
export default Footer;And add some context specific translations keys:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
import Backend from 'i18next-http-backend';
import { DateTime } from 'luxon';
i18n
// i18next-http-backend
// loads translations from your server
// https://github.com/i18next/i18next-http-backend
.use(Backend)
.use(LanguageDetector)
.use(initReactI18next)
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false,
},
resources: {
en: {
translation: {
description: {
part1: 'Edit <1>src/App.js</1> and save to reload.',
part2: 'Learn React'
},
counter_one: 'Changed language just once',
counter_other: 'Changed language already {{count}} times',
footer: {
date: 'Today is {{date, DATE_HUGE}}',
date_morning: 'Good morning! Today is {{date, DATE_HUGE}} | Have a nice day!',
date_afternoon: 'Good afternoon! It\'s {{date, DATE_HUGE}}',
date_evening: 'Good evening! Today was the {{date, DATE_HUGE}}'
}
}
},
de: {
translation: {
description: {
part1: 'Ändere <1>src/App.js</1> und speichere um neu zu laden.',
part2: 'Lerne React'
},
counter_one: 'Die Sprache wurde erst ein mal gewechselt',
counter_other: 'Die Sprache wurde {{count}} mal gewechselt',
footer: {
date: 'Heute ist {{date, DATE_HUGE}}',
date_morning: 'Guten Morgen! Heute ist {{date, DATE_HUGE}} | Wünsche einen schönen Tag!',
date_afternoon: 'Guten Tag! Es ist {{date, DATE_HUGE}}',
date_evening: 'Guten Abend! Heute war {{date, DATE_HUGE}}'
}
}
}
}
});
// new usage
i18n.services.formatter.add('DATE_HUGE', (value, lng, options) => {
return DateTime.fromJSDate(value).setLocale(lng).toLocaleString(DateTime.DATE_HUGE)
});
export default i18n;😁 Yeah, It works!

Separate translations from code
Having the translations in our i18n.js file works, but is not that suitable to work with, for translators.
Let's separate the translations from the code and pleace them in dedicated json files.
Because this is a web application, i18next-http-backend will help us to do so.
npm install i18next-http-backend
Move the translations to the public folder:

Adapt the i18n.js file to use the i18next-http-backend:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
import Backend from 'i18next-http-backend';
import { DateTime } from 'luxon';
i18n
// i18next-http-backend
// loads translations from your server
// https://github.com/i18next/i18next-http-backend
.use(Backend)
.use(LanguageDetector)
.use(initReactI18next)
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false,
}
});
// new usage
i18n.services.formatter.add('DATE_HUGE', (value, lng, options) => {
return DateTime.fromJSDate(value).setLocale(lng).toLocaleString(DateTime.DATE_HUGE)
});
export default i18n;Now the translations are loaded asynchronously, so make sure you wrap your app with a Suspense component to prevent this error: Uncaught Error: App suspended while rendering, but no fallback UI was specified.
import { Suspense } from 'react';
function App() {
// your app's code...
}
// here app catches the suspense from page in case translations are not yet loaded
export default function WrappedApp() {
return (
<Suspense fallback="...is loading">
<App />
</Suspense>
);
}Now your app looks still the same, but your translations are separated. If you want to support a new language, you just create a new folder and a new translation json file. This gives you the possibility to send the translations to some translators. Or if you're working with a translation management system you can just synchronize the files with a cli.
🧑💻 The code of this first part can be found here.
Multiple namespaces
💡 btw: you can also have multiple translation files thanks to the namespaces feature of i18next
One of the advantages of react-i18next is based on i18next, it supports the separation of translations into multiple files - which are called namespaces in i18next.
In order to use multiple namespaces/translation files, you need to specify it when calling useTranslation:
const { t } = useTranslation(['translation', 'common']);
// ...
// t('look.deep', { ns: 'common' })withTranslation(['translation', 'common'])(MyComponent);
// ...
// t('look.deep', { ns: 'common' })or Translation:
<Translation ns={['translation', 'common']}>
{
(t) => <p>{t('look.deep', { ns: 'common' })}</p>
}
</Translation>Better translation management
By sending the translations to some translators or translator agency you have more control and a direct contact with them. But this also means more work for you. This is a traditional way. But be aware sending files around creates always an overhead.
Does a better option exist?
For sure!
i18next helps to get the application translated, and this is great - but there is more to it.
- How do you integrate any translation services / agency?
- How do you keep track of new or removed content?
- How do you handle proper versioning?
- How do you deploy translation changes without deploying your complete application?
- and a lot more...
Looking for something like this❓
- Continuous deployment? Continuous localization!
- Manage the translation files with ease
- Analytics & Statistics
- and a lot more...
How does this look like?
First you need to signup at Locize and login. Then create a new project in Locize and add your translations. You can add your translations either by using the cli or by importing the individual json files or via API.
Done so, we're going to replace i18next-http-backend with i18next-locize-backend.
npm install i18next-locize-backend
After having imported the translations to Locize, delete the locales folder:

Adapt the i18n.js file to use the i18next-locize-backend and make sure you copy the project-id and api-key from within your Locize project:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
import Backend from 'i18next-locize-backend';
import { DateTime } from 'luxon';
const locizeOptions = {
projectId: '0bbc223a-9aba-4a90-ab93-ab9d7bf7f780',
apiKey: 'aaad4141-54ba-4625-ae37-657538fe29e7', // YOU should not expose your apps API key to production!!!
referenceLng: 'en',
};
i18n
// i18next-locize-backend
// loads translations from your project, saves new keys to it (saveMissing: true)
// https://github.com/locize/i18next-locize-backend
.use(Backend)
.use(LanguageDetector)
.use(initReactI18next)
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false,
},
backend: locizeOptions
});
// new usage
i18n.services.formatter.add('DATE_HUGE', (value, lng, options) => {
return DateTime.fromJSDate(value).setLocale(lng).toLocaleString(DateTime.DATE_HUGE)
});
export default i18n;i18next-locize-backend offers a functionality to retrieve the available languages directly from Locize, let's use it:
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
import { useTranslation, Trans } from 'react-i18next';
import { useState, Suspense, useEffect } from 'react';
import Footer from './Footer'
function App() {
const { t, i18n } = useTranslation();
const [count, setCounter] = useState(0);
const [lngs, setLngs] = useState({ en: { nativeName: 'English' }});
useEffect(() => {
i18n.services.backendConnector.backend.getLanguages((err, ret) => {
if (err) return // TODO: handle err...
setLngs(ret);
});
}, []);
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<div>
{Object.keys(lngs).map((lng) => (
<button key={lng} style={{ fontWeight: i18n.resolvedLanguage === lng ? 'bold' : 'normal' }} type="submit" onClick={() => {
i18n.changeLanguage(lng);
setCounter(count + 1);
}}>
{lngs[lng].nativeName}
</button>
))}
</div>
<p>
<i>{t('counter', { count })}</i>
</p>
<p>
<Trans i18nKey="description.part1">
Edit <code>src/App.js</code> and save to reload.
</Trans>
</p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
{t('description.part2')}
</a>
</header>
<Footer t={t} />
</div>
);
}
// here app catches the suspense from page in case translations are not yet loaded
export default function WrappedApp() {
return (
<Suspense fallback="...is loading">
<App />
</Suspense>
);
}save missing translations
Thanks to the use of the saveMissing functionality, new keys gets added to Locize automatically, while developing the app.
Just pass saveMissing: true in the i18next options:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
import Backend from 'i18next-locize-backend';
import { DateTime } from 'luxon';
const locizeOptions = {
projectId: '0bbc223a-9aba-4a90-ab93-ab9d7bf7f780',
apiKey: 'aaad4141-54ba-4625-ae37-657538fe29e7', // YOU should not expose your apps API key to production!!!
referenceLng: 'en',
};
i18n
.use(Backend)
.use(LanguageDetector)
.use(initReactI18next)
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false,
},
backend: locizeOptions,
saveMissing: true
});
// new usage
i18n.services.formatter.add('DATE_HUGE', (value, lng, options) => {
return DateTime.fromJSDate(value).setLocale(lng).toLocaleString(DateTime.DATE_HUGE)
});
export default i18n;Each time you'll use a new key, it will be sent to Locize, i.e.:
<div>{t('new.key', 'this will be added automatically')}</div>will result in Locize like this:
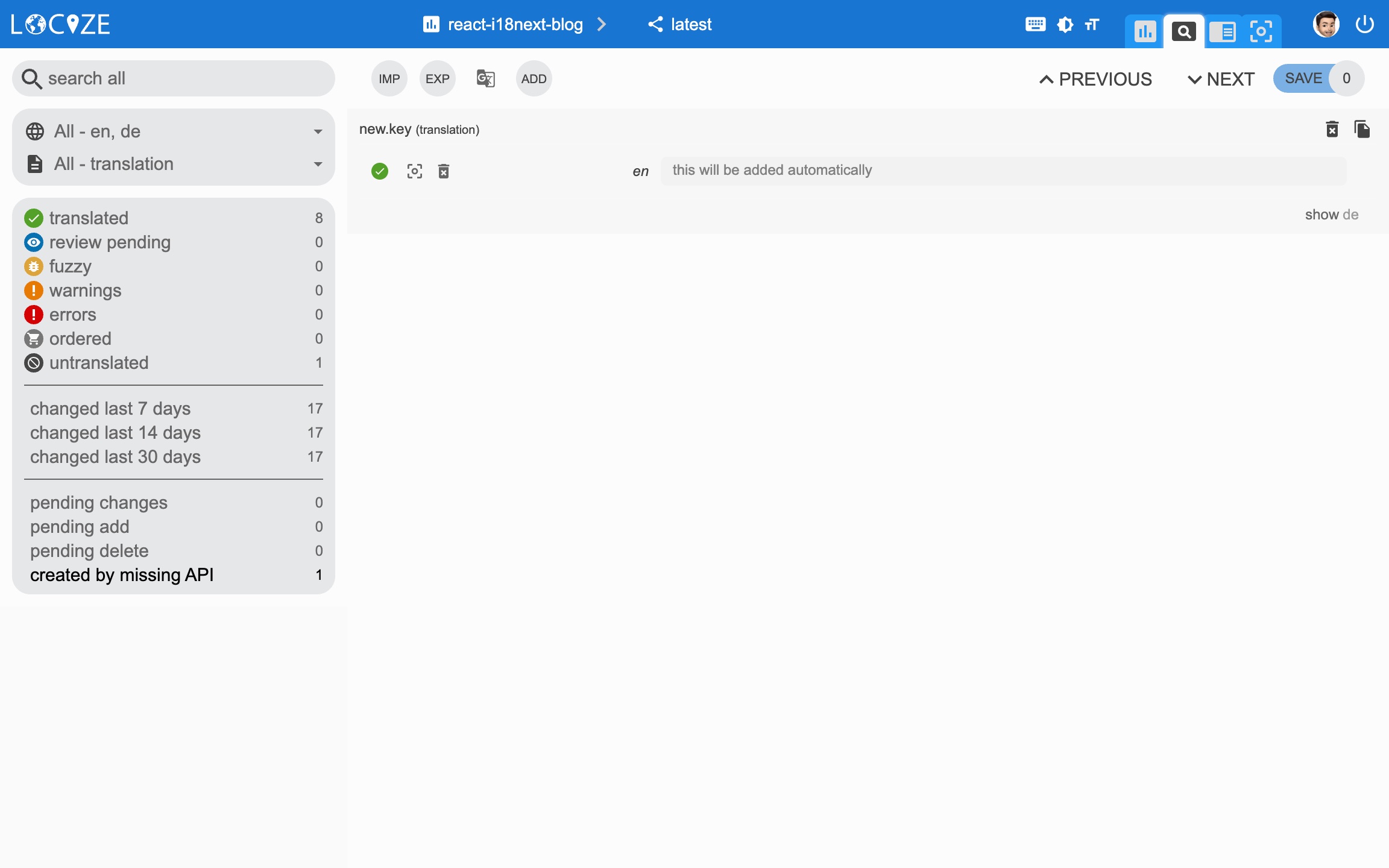
👀 but there's more...
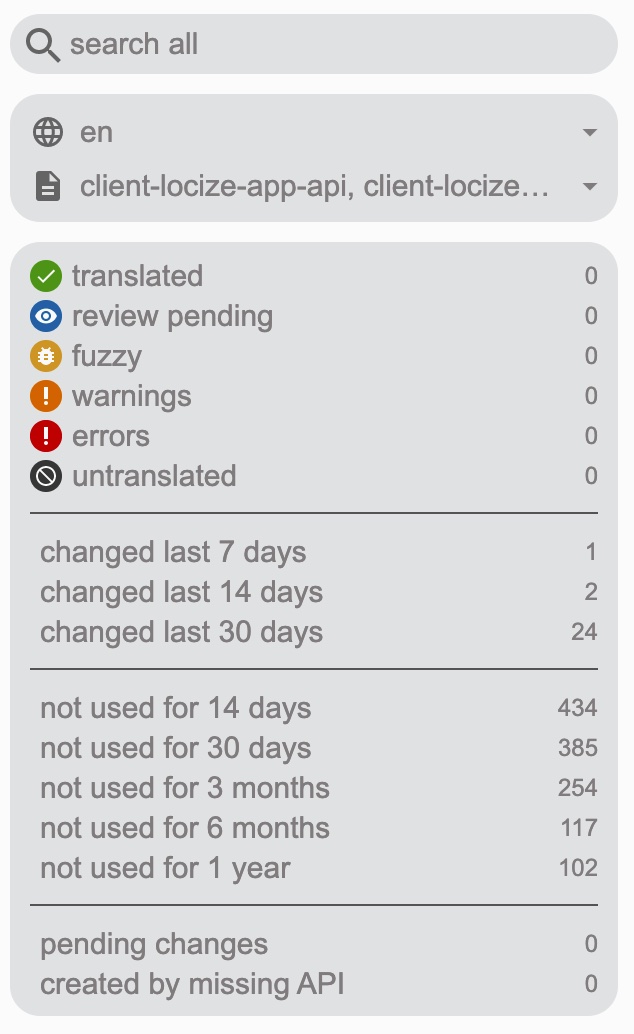
Thanks to the locize-lastused plugin, you'll be able to find and filter in Locize which keys are used or not used anymore.
With the help of the Locize plugin, you'll be able to use your app within the Locize InContext Editor.
Lastly, with the help of the auto-machinetranslation workflow and the use of the saveMissing functionality, new keys not only gets added to Locize automatically, while developing the app, but are also automatically translated into the target languages using machine translation.
Check out this video to see how the automatic machine translation workflow looks like!
npm install locize-lastused locize
use them in i18n.js:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
import Backend from 'i18next-locize-backend';
import LastUsed from 'locize-lastused';
import { locizePlugin } from 'locize';
import { DateTime } from 'luxon';
const locizeOptions = {
projectId: '0bbc223a-9aba-4a90-ab93-ab9d7bf7f780',
apiKey: 'aaad4141-54ba-4625-ae37-657538fe29e7', // YOU should not expose your apps API key to production!!!
referenceLng: 'en',
};
i18n
// locize-lastused
// sets a timestamp of last access on every translation segment on locize
// -> safely remove the ones not being touched for weeks/months
// https://github.com/locize/locize-lastused
.use(LastUsed)
// locize-editor
// InContext Editor of locize
.use(locizePlugin)
// i18next-locize-backend
// loads translations from your project, saves new keys to it (saveMissing: true)
// https://github.com/locize/i18next-locize-backend
.use(Backend)
.use(LanguageDetector)
.use(initReactI18next)
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false,
},
backend: locizeOptions,
locizeLastUsed: locizeOptions,
saveMissing: true
});
// new usage
i18n.services.formatter.add('DATE_HUGE', (value, lng, options) => {
return DateTime.fromJSDate(value).setLocale(lng).toLocaleString(DateTime.DATE_HUGE)
});
export default i18n;Automatic machine translation:
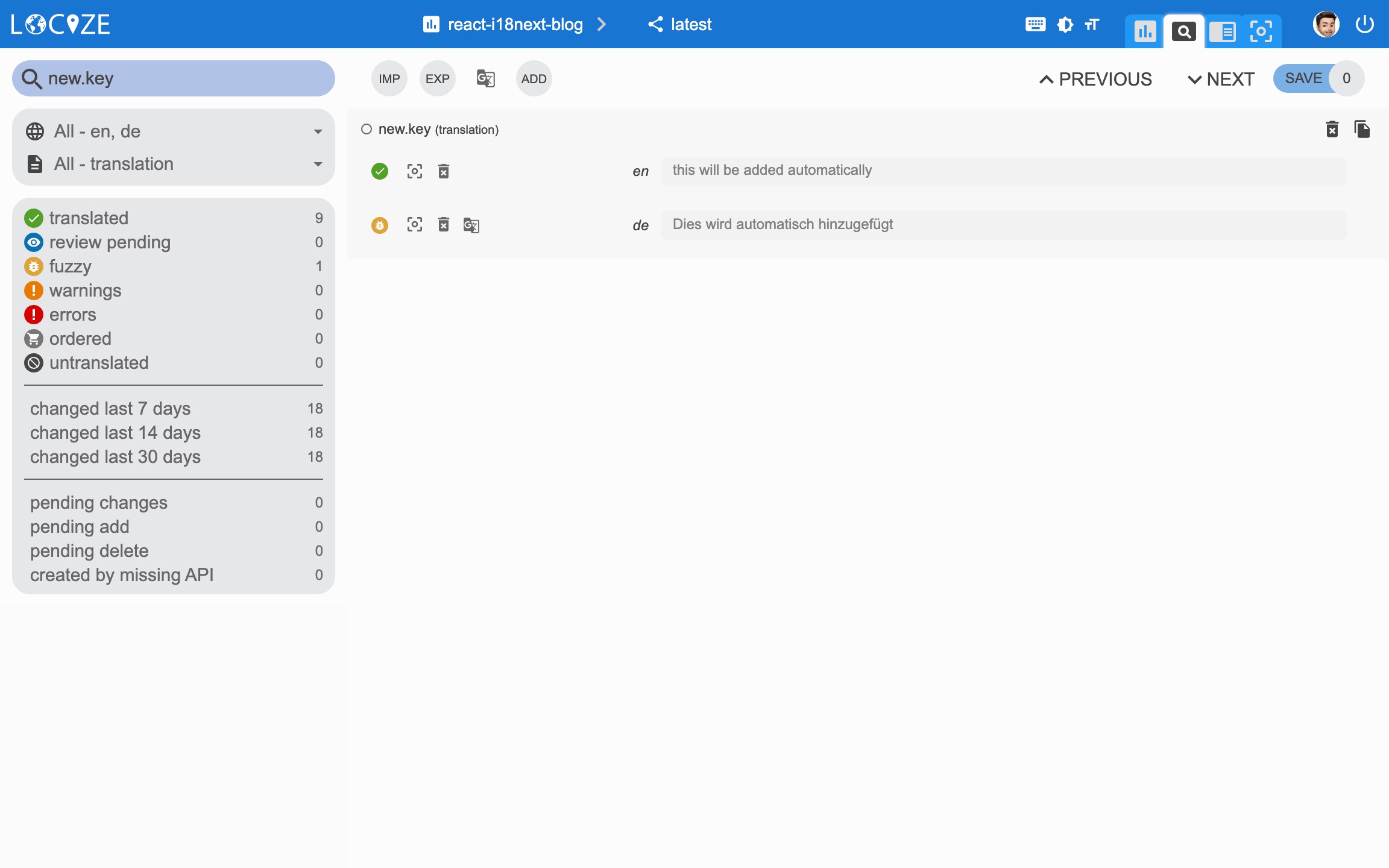
Last used translations filter:
📦 Let's prepare for production 🚀
Now, we prepare the app for going to production.
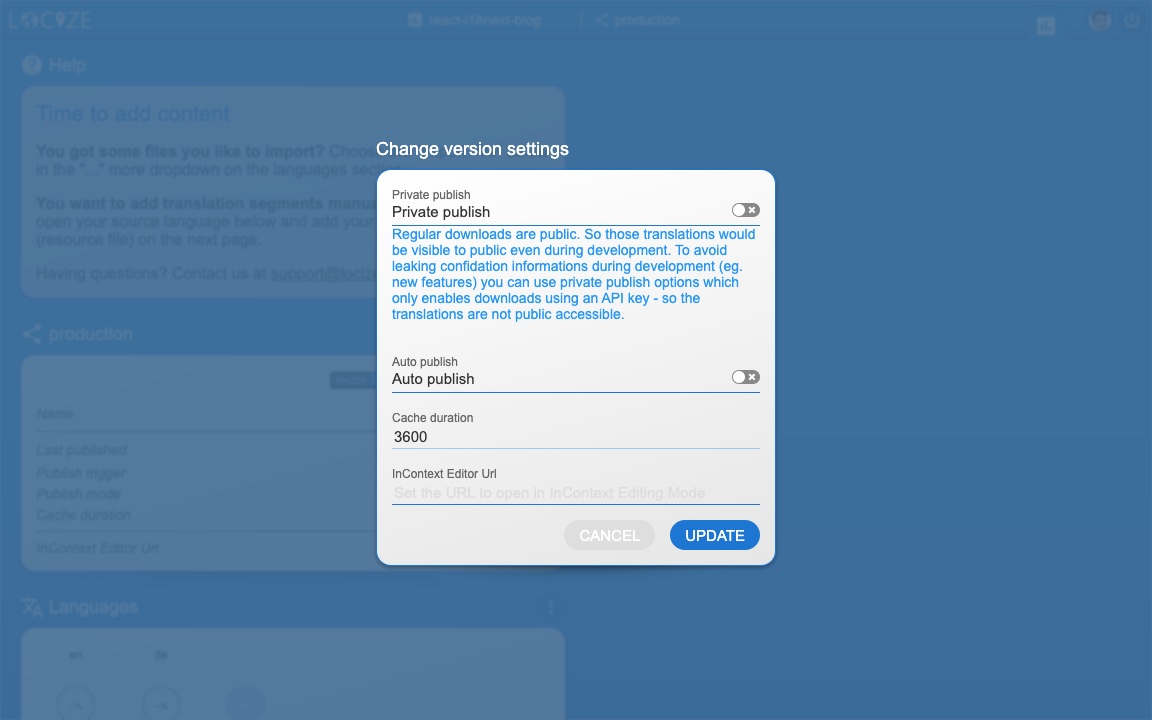
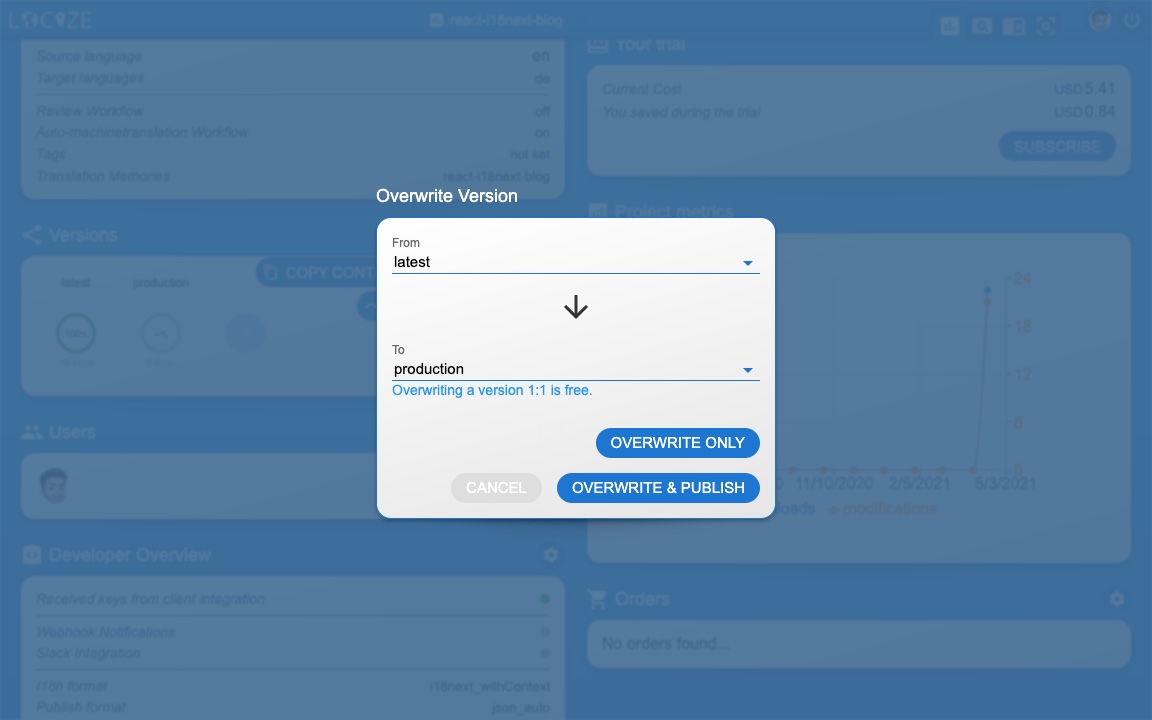
First in Locize, create a dedicated version for production. Do not enable auto publish for that version but publish manually or via API or via CLI. Lastly, enable Cache-Control max-age for that production version.
Let's making use of the environment feature of react-scripts.
Lets' create a default environment file and one for development and one for production:
.env:
SKIP_PREFLIGHT_CHECK=true
REACT_APP_VERSION=$npm_package_version
## locize
REACT_APP_LOCIZE_PROJECTID=0bbc223a-9aba-4a90-ab93-ab9d7bf7f780
REACT_APP_LOCIZE_REFLNG=en.env.development:
REACT_APP_LOCIZE_VERSION=latest
REACT_APP_LOCIZE_APIKEY=aaad4141-54ba-4625-ae37-657538fe29e7.env.production:
REACT_APP_LOCIZE_VERSION=productionNow let's adapt the i18n.js file:
import i18n from 'i18next';
import { initReactI18next } from 'react-i18next';
import LanguageDetector from 'i18next-browser-languagedetector';
import Backend from 'i18next-locize-backend';
import LastUsed from 'locize-lastused';
import { locizePlugin } from 'locize';
import { DateTime } from 'luxon';
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production';
const locizeOptions = {
projectId: process.env.REACT_APP_LOCIZE_PROJECTID,
apiKey: process.env.REACT_APP_LOCIZE_APIKEY, // YOU should not expose your apps API key to production!!!
referenceLng: process.env.REACT_APP_LOCIZE_REFLNG,
version: process.env.REACT_APP_LOCIZE_VERSION
};
if (!isProduction) {
// locize-lastused
// sets a timestamp of last access on every translation segment on locize
// -> safely remove the ones not being touched for weeks/months
// https://github.com/locize/locize-lastused
i18n.use(LastUsed);
}
i18n
// locize-editor
// InContext Editor of locize
.use(locizePlugin)
// i18next-locize-backend
// loads translations from your project, saves new keys to it (saveMissing: true)
// https://github.com/locize/i18next-locize-backend
.use(Backend)
.use(LanguageDetector)
.use(initReactI18next)
.init({
debug: true,
fallbackLng: 'en',
interpolation: {
escapeValue: false,
},
backend: locizeOptions,
locizeLastUsed: locizeOptions,
saveMissing: !isProduction // you should not use saveMissing in production
});
// new usage
i18n.services.formatter.add('DATE_HUGE', (value, lng, options) => {
return DateTime.fromJSDate(value).setLocale(lng).toLocaleString(DateTime.DATE_HUGE)
});
export default i18n;Now, during development, you'll continue to save missing keys and to make use of lastused feature. => npm run start
And in production environment, saveMissing and lastused are disabled, and also the api-key is not exposed. => npm run build && npm run serve
🧑💻 The complete code for this React example can be found here. And a TypeScript version here.
Check also the code integration part in this YouTube video.
There's also an i18next crash course video.
There is also a Spanish translation of this blog post.
🎉🥳 Congratulations 🎊🎁
I hope you’ve learned a few new things about i18next, React.js localization and modern localization workflows.
So if you want to take your i18n topic to the next level, it's worth trying the localization management platform - Locize.
The founders of Locize are also the creators of i18next. So by using Locize you directly support the future of i18next.
